Here Is How to Craft Your Story as A Liberal!
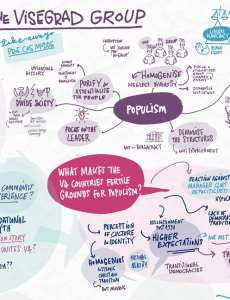
If you look at the political map of Europe these days, you cannot miss the distinctive success of populist movements in Central Europe, not to mention the alliance of Hungarian and Polish governments. With a group of participants from the region, we discussed populism in the Visegrád (V4) countries and its relevance for political communication during the online workshop series “The Story of Visegrád”.

























